Publications
Group highlights
(For a full list of publications see below or go to Google Scholar, ResearcherID or pubmed)

Posttranslational modification (PTM) regulates protein activity by attaching chemical groups to amino acids in an enzymatic or non-enzymatic manner. PTMs offer fast and dynamic regulation of protein expression and can be influenced by specific dietary components that induce PTM events in gut microbiomes and their hosts. PTMs on microbiome proteins have been found to contribute to host-microbe interactions.
Lirit Duchovni, Genrieta Shmunis, Lior Lobel
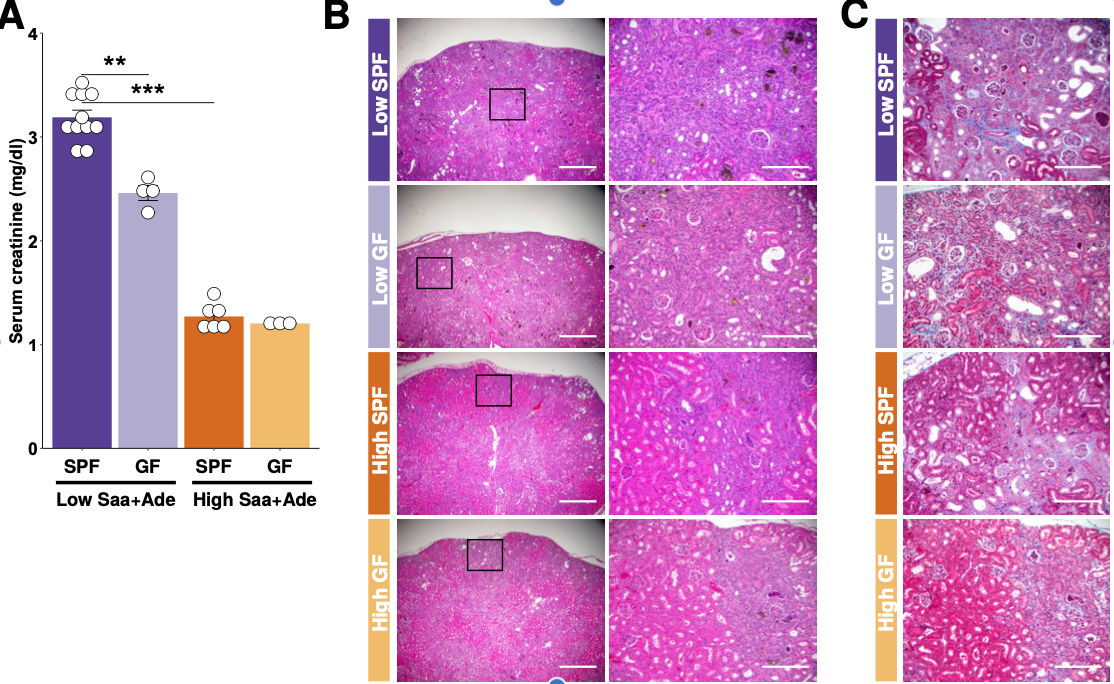
Associations between chronic kidney disease (CKD) and the gut microbiota have been postulated, yet questions remain about the underlying mechanisms. In humans, dietary protein increases gut bacterial production of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), indole, and indoxyl sulfate. The latter are uremic toxins, and H2S has diverse physiological functions, some of which are mediated by posttranslational modification. In a mouse model of CKD, we found that a high sulfur amino acid-containing diet resulted in posttranslationally modified microbial tryptophanase activity. This reduced uremic toxin-producing activity and ameliorated progression to CKD in the mice. Thus, diet can tune microbiota function to support healthy host physiology through posttranslational modification without altering microbial community composition.
Lior Lobel, Y Grace Cao, Kathrin Fenn, Jonathan N Glickman, Wendy S Garrett
Science 369, Sep 2020, 369(6510)
Full List of publications
Posttranslational modifications: an emerging functional layer of diet-host-microbe interactions
Lirit Duchovni, Genrieta Shmunis, Lior Lobel
mBio, Sep 10 2024, 15(10)
Diet posttranslationally modifies the mouse gut microbial proteome to modulate renal function
Lior Lobel, Y Grace Cao, Kathrin Fenn, Jonathan N Glickman, Wendy S Garrett
Science 369, Sep 2020, 369(6510)
Butyrate Makes Macrophages ‘Go Nuclear’ against Bacterial Pathogens
Lior Lobel, Wendy S Garrett
Comment in Immunity, 2019 Feb 19
Controlled branched-chain amino acids auxotrophy in Listeria monocytogenes allows isoleucine to serve as a host signal and virulence effector
Moran Brenner, Lior Lobel, Ilya Borovok, Nadejda Sigal, Anat A Herskovits
PLoS Genetics, 2018 Mar 12;14(3):e1007283.
Take DAT, Flu!
Lior Lobel, Wendy S Garrett
Comment in Immunity, 2017 Sep 19
Metabolic Genetic Screens Reveal Multidimensional Regulation of Virulence Gene Expression in Listeria monocytogenes and an Aminopeptidase That Is Critical for PrfA Protein Activation
Sivan Friedman, Marika Linsky, Lior Lobel, Lev Rabinovich, Nadejda Sigal, Anat A Herskovits
Infection and Immunity, 2017, May 23
L-glutamine Induces Expression of Listeria monocytogenes Virulence Genes
Adi Haber, Sivan Friedman, Lior Lobel, Tamar Burg-Golani, Nadejda Sigal, Jessica Rose, Nurit Livnat-Levanon, Oded Lewinson, Anat A Herskovits
PLoS Pathogens 2017, Jan 23
Systems Level Analyses Reveal Multiple Regulatory Activities of CodY Controlling Metabolism, Motility and Virulence in Listeria monocytogenes
Lior Lobel, Anat A Herskovits
PLoS Genetics, 2016, Feb 19
The metabolic regulator CodY links Listeria monocytogenes metabolism to virulence by directly activating the virulence regulatory gene prfA
Lior Lobel, Nadejda Sigal, Ilya Borovok, Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein, Anat A Herskovits
Molecular Microbiol, 2015 Feb
Listeria monocytogenes MDR transporters are involved in LTA synthesis and triggering of innate immunity during infection
Keren Tadmor, Yair Pozniak, Tamar Burg Golani, Lior Lobel, Moran Brenner, Nadejda Sigal, Anat A Herskovits
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiolgy, 2014 Feb
Integrative genomic analysis identifies isoleucine and CodY as regulators of Listeria monocytogenes virulence
Lior Lobel, Nadejda Sigal, Ilya Borovok, Eytan Ruppin, Anat A Herskovits
PLoS Genetics, 2012, Sep
